The New Reality for SaaS Companies
SaaS companies have transformed how businesses operate, streamlining workflows, scaling faster, and eliminating the need for heavy infrastructure. But with widespread adoption comes a new reality—intense competition and rapidly shifting expectations.
As the SaaS model matured, it triggered the rise of adjacent services like DaaS, PaaS, and iPaaS—each expanding the cloud ecosystem and offering new layers of functionality. These innovations aren’t just trends—they’re redefining what SaaS companies must deliver to stay relevant.
For small and mid-sized players, this diversification opens real opportunities. Instead of competing head-to-head with tech giants, these SaaS companies can carve out specialized niches, offering focused solutions tailored to evolving market needs.
Today, SaaS is no longer a standalone offering. It’s the foundation of a much broader, interconnected landscape—one that demands agility, innovation, and a relentless focus on solving real problems (Learn how we can help your SaaS Business: Click Here).
Key Milestones in SaaS Popularity (and DaaS, PaaS, and iPaaS)
- 1990s – Early Concepts: SaaS began with the Application Service Provider (ASP) model.
- Early 2000s – Emergence: Broadband made SaaS a viable alternative to on-premise software. DaaS emerges as a concept – so did PaaS and iPaaS.
- Mid-2000s – Growth: Cloud infrastructure improved, and businesses embraced SaaS for cost savings, scalability, and easy deployment.
- Late 2000s – Mainstream: Companies moved to the cloud to reduce hardware costs and maintenance. DaaS started to grow – so did PaaS and iPaaS.
- 2010s – Dominance: SaaS became the primary software delivery model as the industry matured.
- 2020s – Norm: SaaS became the standard across industries due to its flexibility and lower infrastructure costs. DaaS matured and gained popularity – so did PaaS and iPaaS
- Mid-2020s – Diversification: SaaS continues to evolve, with new models and solutions emerging.
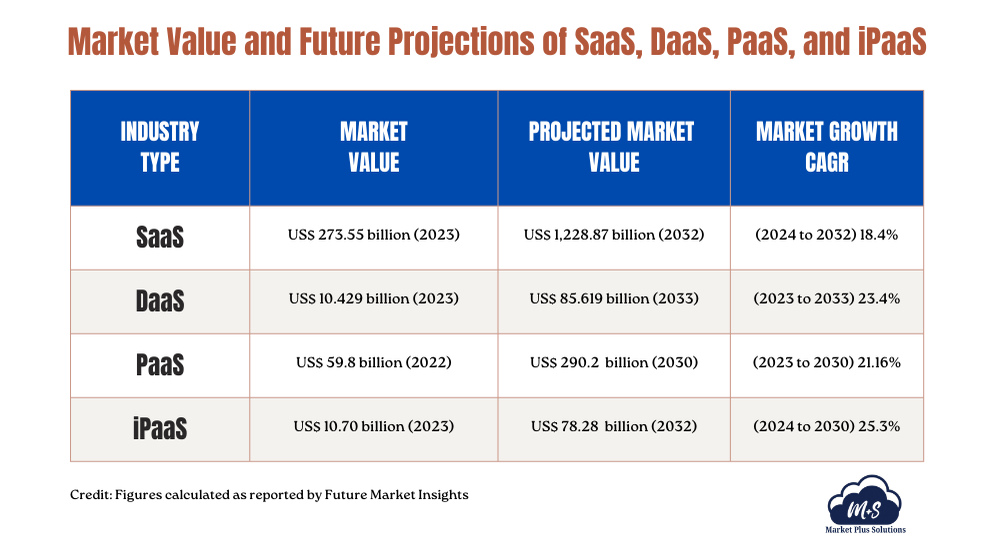
Differences Between SaaS, DaaS, PaaS and iPaaS
SaaS (Software as a Service), DaaS (Data as a Service), PaaS (Platform as a Service), and iPaaS (Integration Platform as a Service) are all cloud service models (See how our content marketing and SEO services can accelerate your SaaS growth: Click here). However, they serve different purposes.
Here’s a comparison of these services:
SaaS (Software as a Service)
SaaS provides complete software applications over the internet. Users access software hosted on the cloud without needing to install or maintain it on their local devices.
- Target Audience: End-users who need a ready-to-use application.
- Key Features:
- Fully functional applications.
- Accessible via a web browser or mobile apps.
- Managed by the service provider.
- Use Case: When businesses or individuals need an out-of-the-box software solution without worrying about infrastructure or software management.
DaaS (Data as a Service)
DaaS offers data storage, processing, and analytics services through the cloud. It allows businesses to access and manage data remotely and use it for insights and analytics.
- Target Audience: Companies needing centralized, secure, and scalable data access without investing in physical infrastructure.
- Key Features:
- Provides access to data and data processing services via the cloud.
- Often includes data management, analytics, and security.
- Pay-as-you-go pricing based on data usage or access.
- Use Case: Ideal for businesses requiring real-time data access, data warehousing, or business intelligence without managing their own data infrastructure.
PaaS (Platform as a Service)
PaaS provides a platform for developers to build, test, and deploy applications. It offers infrastructure, development tools, and databases in a managed environment.
- Target Audience: Developers and IT teams who want to build custom applications without managing underlying hardware or software layers.
- Key Features:
- Offers development frameworks, databases, middleware, and hosting.
- Simplifies app development by removing infrastructure management concerns.
- Scalable infrastructure to accommodate app growth.
- Use Case: Suitable for organizations or developers building custom apps where they want to focus on coding rather than managing servers or networks.
iPaaS (Integration Platform as a Service)
iPaaS provides tools for integrating various software applications, services, and data from different environments (cloud and on-premises). It automates and simplifies workflows between these systems.
- Target Audience: Businesses needing to integrate multiple applications or data sources across different systems for seamless communication and automation.
- Key Features:
- Connects cloud apps, databases, APIs, and on-premises systems.
- Offers pre-built connectors and automation tools.
- Streamlines data flow, enabling businesses to automate processes across multiple platforms.
- Use Case: Useful for businesses that rely on multiple SaaS or on-premises applications and need to synchronize data, automate workflows, or enable cross-application functionality.
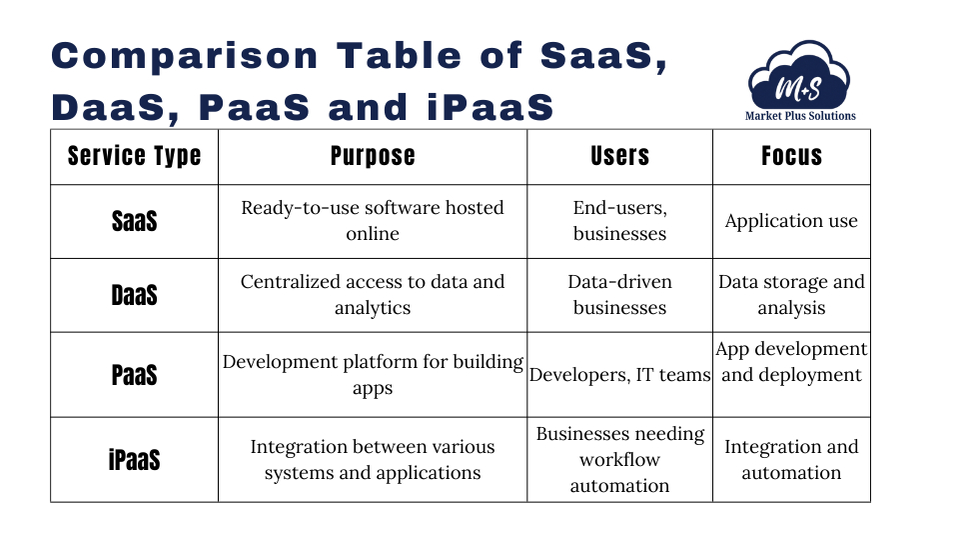
How SaaS Compares to DaaS, PaaS and iPaaS:
Are DaaS, PaaS, and iPaaS part of SaaS? Not exactly. While they all operate within the broader cloud ecosystem, each serves a distinct purpose—and none replace what SaaS companies deliver. These services have emerged in response to evolving business needs, often working alongside SaaS products rather than overlapping with them.
In fact, many SaaS companies rely on these technologies to enhance their offerings (Visit our services page to see how we turn content into growth for SaaS businesses: Click Here). A CRM platform, for example, might pull customer data from a DaaS provider, run on a PaaS infrastructure, and use iPaaS to integrate with third-party tools.
Here’s how they stack up:
SaaS vs DaaS: SaaS delivers complete applications to end users—think email platforms or project management tools. DaaS, on the other hand, delivers data. It’s backend-focused, powering analytics and storage rather than user interaction.
SaaS vs PaaS: SaaS gives users finished software. PaaS offers developers a framework to build applications. While SaaS is ready to use, PaaS is a foundation for creation.
SaaS vs iPaaS: SaaS is about individual tools. iPaaS connects those tools. It enables automation and integration across multiple platforms, helping businesses streamline workflows between different SaaS solutions.

Why SaaS Companies Are Watching iPaaS and DaaS Closely
While SaaS has long been the dominant model in cloud software, iPaaS and DaaS are quickly emerging as the new frontrunners. Driven by the rise of automation, real-time analytics, and AI, these models are reshaping how businesses manage data and integration.
So, what’s behind the surge?
iPaaS is now critical for companies juggling multiple cloud tools. It connects and automates systems, allowing for seamless data flow and improved efficiency across the stack.
DaaS is gaining ground as the demand for clean, accessible, and actionable data explodes—especially for AI and machine learning use cases.
These shifts aren’t just trends—they signal where the market is heading. SaaS companies that embrace DaaS and iPaaS as part of their ecosystem strategy will be better positioned to scale, adapt, and lead in a data-first, automation-driven world.
Shift from SaaS Toward DaaS, PaaS, and iPaaS:
The SaaS market has become crowded, with fierce competition and growing demand. In response, many SaaS companies are broadening their services or shifting towards DaaS, PaaS, and iPaaS to capitalize on new opportunities and meet evolving customer needs by offering more integrated and scalable solutions. SaaS remains the core focus—it is the services that are being diversified. Additionally, customers now seek more customized and flexible features, prompting SaaS companies to prioritize client retention and diversify revenue streams as essential growth strategies (Learn how our tailored Content Marketing strategies drive real results for SaaS companies like yours).
Here’s why some SaaS companies have made these shifts and how it has driven many small and medium-sized businesses to capitalize on the opportunity:
SaaS to DaaS
Many SaaS companies generate large volumes of valuable data through their software offerings. By moving toward DaaS, they can monetize this data, offering clients valuable insights and enabling better data-driven decision-making.
- How They Are Transitioning:
- Data-Driven Services: SaaS companies are adding data-centric services such as advanced analytics, predictive models, and real-time reporting to enhance their software products.
- API Access to Data: Some companies offer data access via APIs, allowing customers to tap into their data for customized solutions or to integrate into existing systems.
- Data Marketplaces: SaaS providers create data marketplaces where users can purchase datasets for analytics, business intelligence, or machine learning models.
SaaS to PaaS (Platform as a Service)
As customers seek more customization and flexibility, SaaS companies are moving toward PaaS to allow developers to build custom applications on their platforms, creating an ecosystem that extends the core software’s functionality.
- How They Are Transitioning:
- Opening Up Platforms: SaaS companies are offering their software as a platform, allowing developers to create custom apps or extend functionalities using APIs, SDKs, and development tools.
- Offering Development Environments: By providing development environments (such as sandboxes or IDEs), SaaS companies encourage customers to build tailored applications that integrate seamlessly with the SaaS solution.
- Third-Party App Ecosystems: Creating ecosystems where third-party developers can build and sell apps on the platform, adding value for end-users and creating new revenue streams for the SaaS provider.
SaaS to iPaaS (Integration Platform as a Service)
As businesses adopt more cloud services, the need to integrate various applications into seamless workflows has increased. SaaS companies are moving toward iPaaS to offer enhanced integration capabilities, allowing users to automate and streamline data flows across different applications.
- How They Are Transitioning:
- Integration Layers: SaaS companies are adding integration layers to their products, allowing users to connect their software with other third-party tools. This enables smooth data exchange and workflow automation.
- Offering Pre-Built Connectors: Many SaaS providers are building pre-configured connectors to popular apps (like Salesforce, Google Workspace, or Slack) so businesses can integrate their existing tools with ease.
- Developing Automation Tools: SaaS companies integrate workflow automation and orchestration tools to help businesses create seamless, end-to-end processes without manual intervention.
Top Five Key Trends Shaping the Future of SaaS
In addition to business diversification, several key trends are shaping the future of the SaaS industry. While rising market demands are driving business opportunities, other crucial factors are currently influencing—and are expected to continue shaping—the direction of SaaS as we head into 2024 and beyond.
AI’s Growing Influence:
AI is transforming SaaS with automation, analytics, and machine learning, enabling smarter, more personalized solutions. As AI advances, it will further shape SaaS by anticipating user needs and boosting productivity.
Personalization as a Key Differentiator:
With increasing competition, personalization is crucial. Customers now expect tailored experiences, and SaaS companies that provide customized solutions will have a competitive edge.
Increasing Flexibility:
SaaS flexibility has drastically improved, allowing seamless integration of multiple tools. This empowers businesses to create custom tech stacks, driving demand for solutions like iPaaS.
Cybersecurity Challenges Fueling Diversifications:
As SaaS becomes more interconnected, cybersecurity risks rise. This will likely drive new diversifications, with companies focusing on enhanced security features and services.
Maturation of White-Label Solutions:
White-label SaaS has matured, offering flexibility, competitive pricing, and customization. This has enabled smaller companies and entrepreneurs to enter the market and provide specialized services.
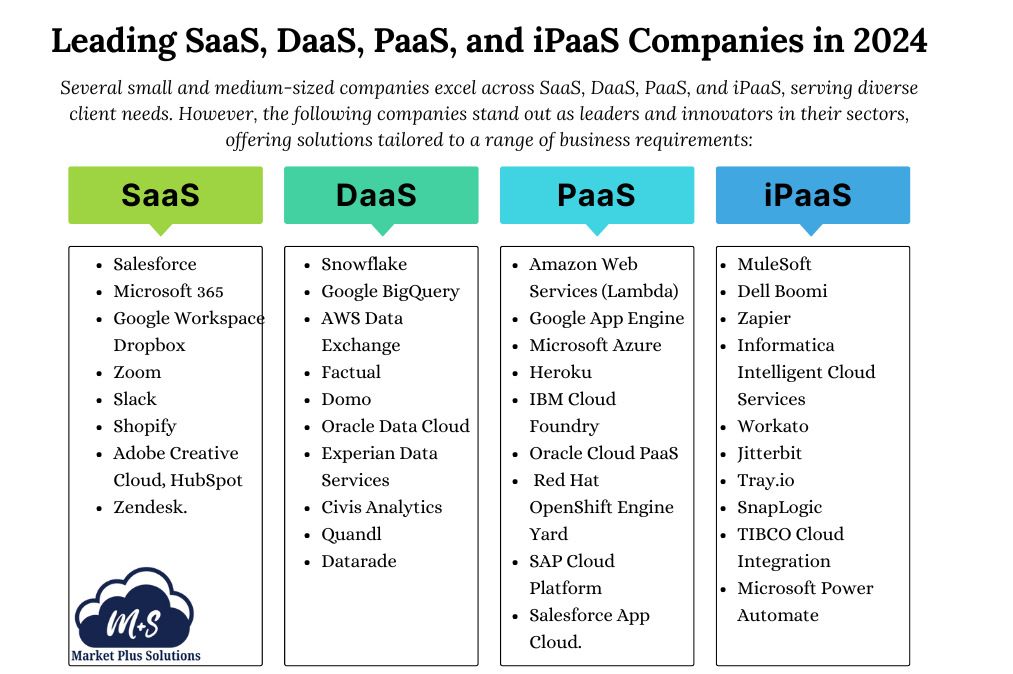
The Rise of Micro SaaS
One of the most exciting developments in the SaaS space is the rise of Micro SaaS—lean, niche-driven products often created by small teams or even solo founders. Unlike traditional SaaS companies that target broad markets, Micro SaaS products focus on solving very specific problems for highly targeted user groups. Their power lies in precision, agility, and the ability to deliver real value without unnecessary complexity.
Despite operating on a smaller scale, Micro SaaS businesses are proving to be highly profitable. Their laser focus allows them to serve customers with exactly what they need—nothing more, nothing less. As demand grows for tailored, lightweight solutions, Micro SaaS is becoming a significant force in the evolution of the broader SaaS industry (Our customized SEO Services can help your Micro SaaS Business: Click Here).
This shift is also driving growth in connected services like DaaS, PaaS, and iPaaS. These platforms provide the technical backbone that many Micro SaaS products depend on—whether it’s for storage, development, or integration. As this ecosystem grows, SaaS companies that embrace these technologies will be better equipped to scale smarter and faster.
In this changing environment, SaaS companies must rethink their role—not just as software vendors, but as solution architects. The future favors those that can stay lean, move fast, and deliver exactly what their audience needs.
Conclusion: The Future for SaaS Companies
The SaaS landscape has evolved far beyond its original framework. Today, SaaS companies are no longer just building software—they’re building ecosystems. With the rise of DaaS, PaaS, and iPaaS, the market is shifting toward more connected, data-driven, and flexible solutions. SaaS companies that recognize this shift and integrate these complementary services into their strategy will be far better positioned for long-term success.
At the same time, the emergence of Micro SaaS shows how even the smallest SaaS companies can make a major impact by solving specific, high-value problems. These agile players are pushing the entire industry forward, creating demand for more seamless data integration, automation, and platform extensibility.
The future belongs to SaaS companies that adapt, specialize, and build intelligently within this broader cloud ecosystem. Whether you’re a startup or scaling enterprise, the opportunity is clear: innovate with purpose, stay close to your market, and use the evolving landscape to your advantage. Contact us if your SaaS Business needs a little push from a digital marketing agency.

